OUR RESULTS
The results are transformative - families will see measurable changes in attitude, confidence and school progress.
See Our ResultsFor decades the Mathnasium Method™ has transformed the way children learn maths. We build a foundation for maths mastery through deep understanding by starting with what they already know, addressing any learning gaps, expanding their mathematical thinking, and adding new concepts in sequence. This proprietary method works for students of all ages and skill levels, whether they’re struggling in maths, doing okay but could be doing better, or are already excelling but need more of a challenge. When children see what they can achieve because of their proficiency in maths, it can alter the course of their entire lives.
This is the key to success in maths—the understanding of what numbers mean and how they work together. And Number Sense isn't just for young children. We work on these topics through the levels shown below before moving on to Algebra and other higher maths disciplines.
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forwards and backwards.
Wholes And Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem solving.
Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”
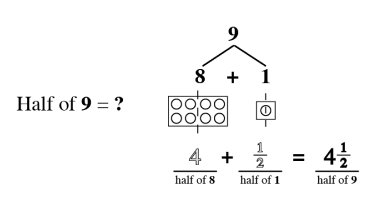
Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.

The Law of SAMEness
The Law of Sameness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.
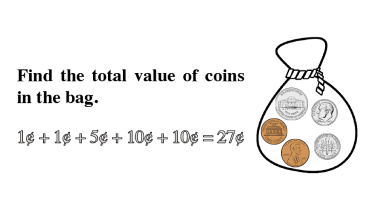
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forwards and backwards.
Wholes and Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem solving.
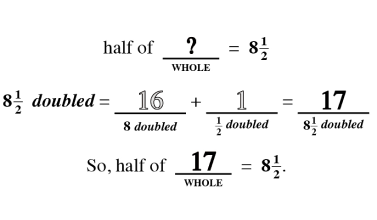
Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”

Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.

The Law of SAMEness
The Law of Sameness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.
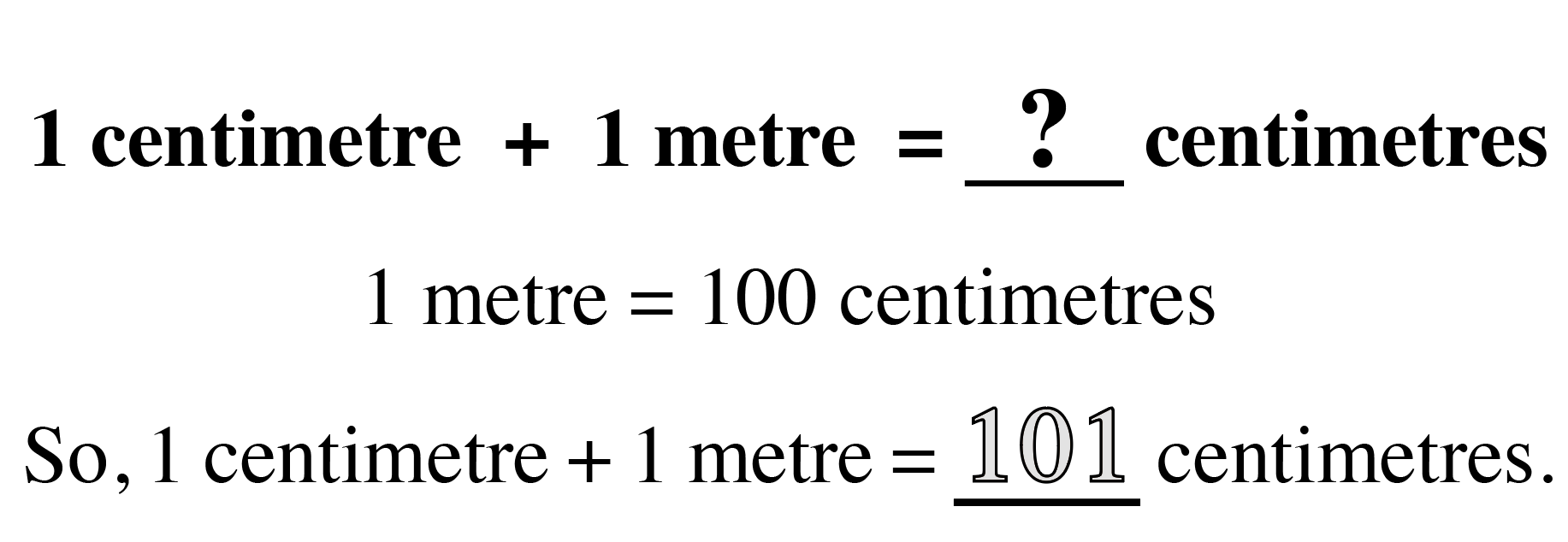
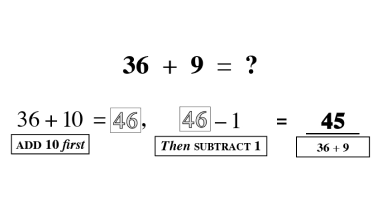
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forwards and backwards.
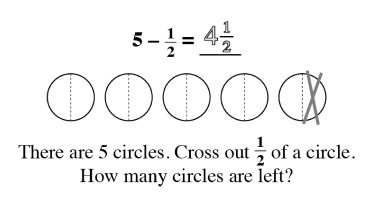
Wholes and Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem solving.
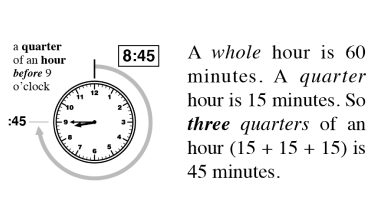
Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”
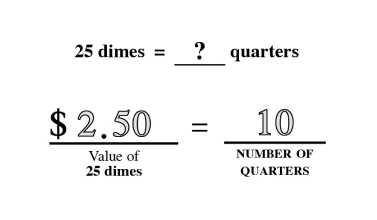
Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.

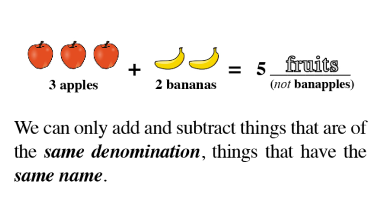
The Law of SAMEness
The Law of Sameness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forwards and backwards.
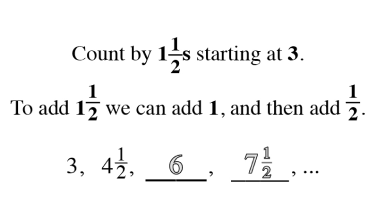
Wholes and Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem solving.
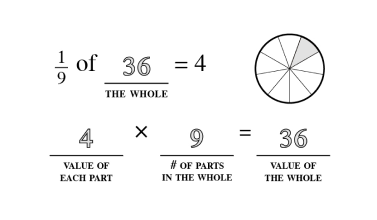
Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”
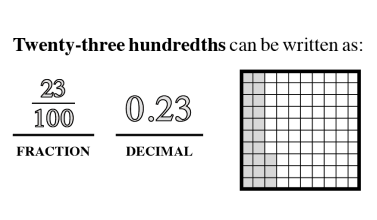
Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.

The Law of SAMEness
The Law of Sameness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.
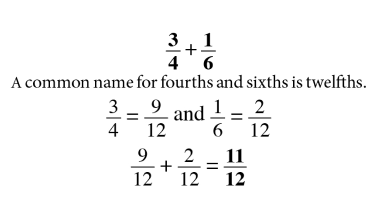
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forwards and backwards.
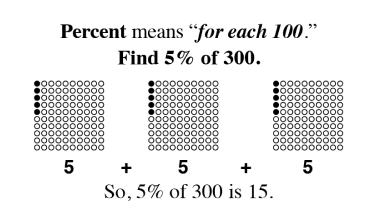
Wholes and Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem solving.

Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”
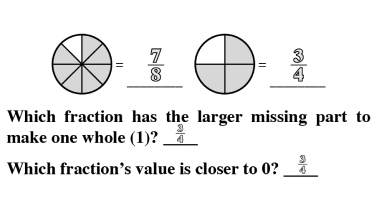
Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.
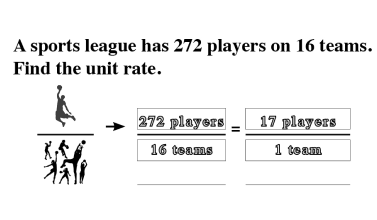
The Law of SAMEness
The Law of Sameness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.
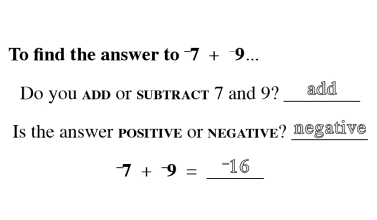
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forward and backward.
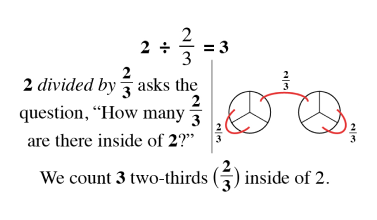
Wholes and Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem-solving.
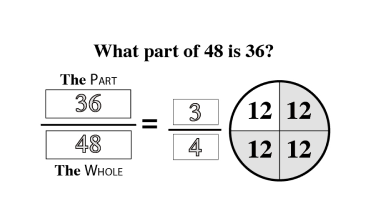
Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”

Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.
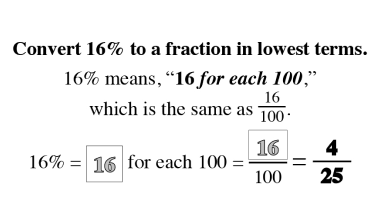
The Law of SAMEness
The Law of Sameness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.
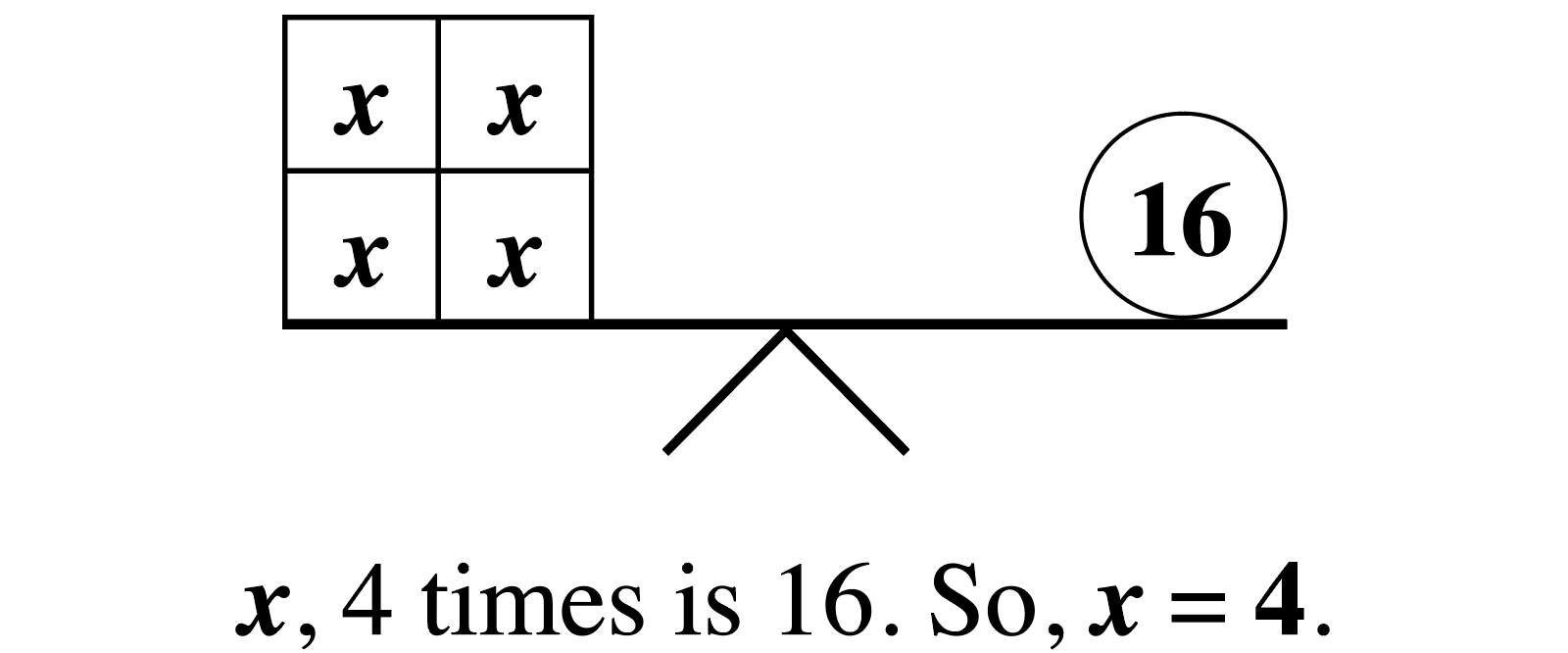
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forward and backward.

Wholes and Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem-solving.
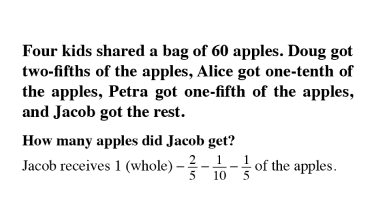
Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”

Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.

The Law of SAMEness
The Law of SAMEness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.
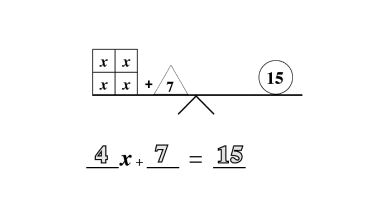
Counting
Counting is the key to unlocking addition and subtraction in early maths development. At Mathnasium, our initial goal is to have a student become comfortable with counting to any number, from any number, by any number, forward and backward.

Wholes and Parts
As students begin to understand the relationship between a whole and the parts, a world of mathematical concepts and exercises can be explored. Once students have mastered these skills, they have little trouble with algebraic problem-solving.
Quantity and Denomination
The quantity and denomination construct examines two aspects of numerical value. Quantity asks “how many?” and denomination asks “of what?”

Proportional Thinking
Proportional thinking established a fundamental base that leased to a stronger understanding of critical concepts like ratio, direct and indirect variation and algebraic reasoning.
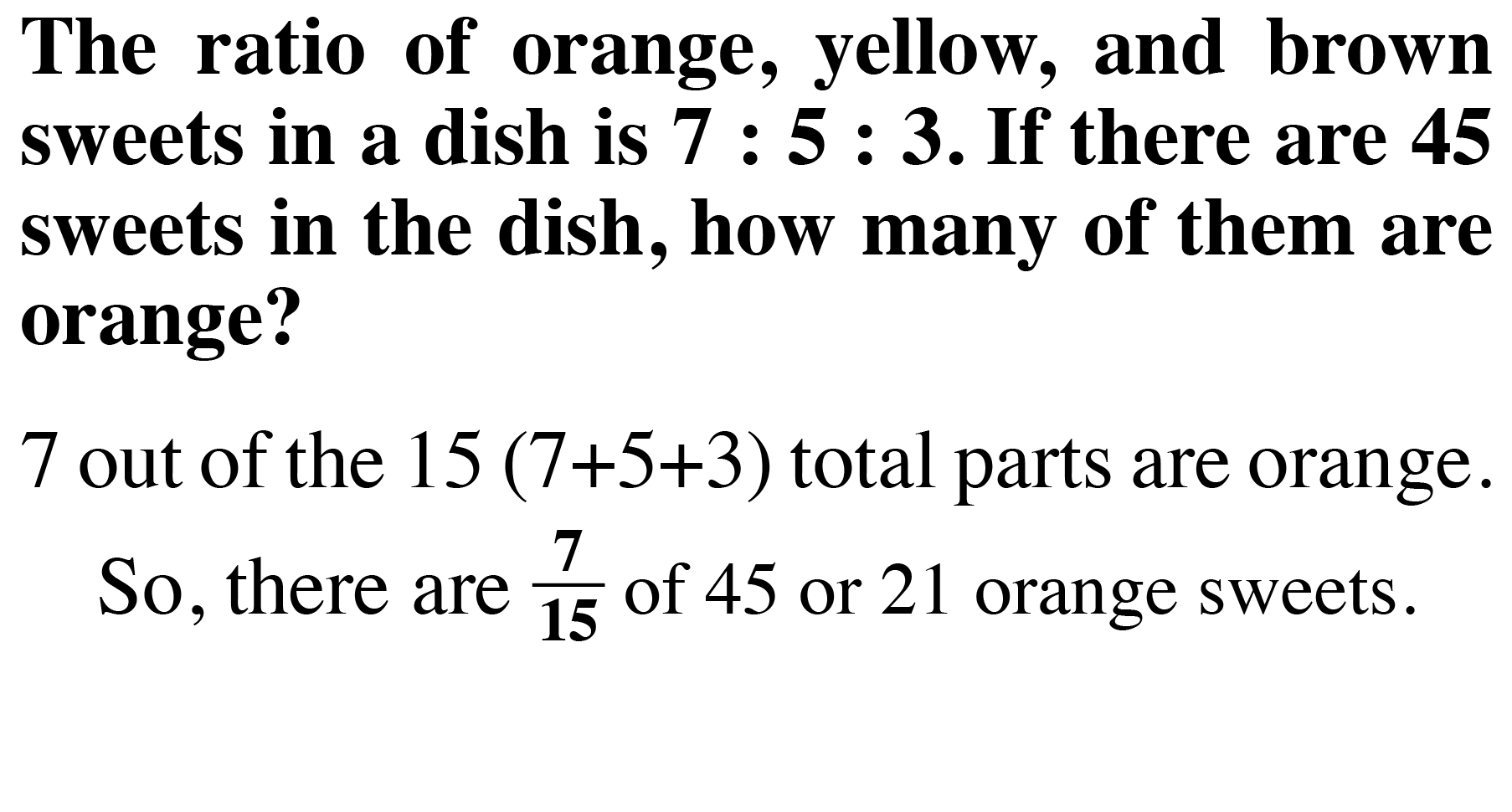
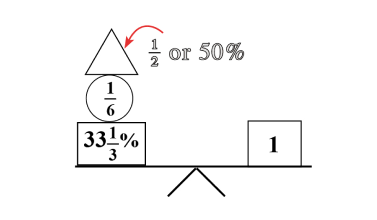
The Law of SAMEness
The Law of SAMEness is a concept students naturally apply in their reasoning without being aware of it. For example, quantities of apples and bananas cannot be added together unless first being changed so that they have the same name, which is fruit.

We use a combination of mental, verbal, visual, tactile and written techniques to build maths knowledge level by level, so they understand it, master it and enjoy it.





The results are transformative - families will see measurable changes in attitude, confidence and school progress.
See Our Resultsof parents report an improvement in their child’s maths skills and understanding.
of parents report improved attitude towards maths after attending Mathnasium.
of students saw an improvement in their school grades.



Maths went from being a seemingly insurmountable challenge for our son to being one of his strongest subjects in school.
Loreana C., Parent





Teachers are fantastic in helping my kid in his Maths score. He has now improved massively from barely passing...





My son has been with Mathnasium for a year, and I’ve witnessed tremendous improvement in his math skills and a...
With over 1,100 centres globally, find a centre near you
It’s as easy as:

